While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in understanding and responding to complex queries, their reliance on server-side processing poses significant challenges for mobile assistants. These challenges primarily revolve around two key issues: Privacy: Mobile assistants frequently require access to sensitive personal information to provide accurate and relevant responses. Storing and processing this...
Category: Science
Unmasking the Mathematical Minds of LLMs: Are They Really Reasoning?
Large language models (LLMs) have stormed onto the scene, dazzling us with their linguistic prowess and seeming intelligence. From crafting creative text formats to tackling complex coding challenges, they've left many wondering: are these machines truly thinking? The spotlight, in particular, has fallen on their mathematical reasoning abilities, with many claiming these models are on...
Can AI talk us out of conspiracy theory rabbit holes?
New research published in Science shows that for some people who believe in conspiracy theories, a fact-based conversation with an artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot can “pull them out of the rabbit hole”. Better yet, it seems to keep them out for at least two months. This research, carried out by Thomas Costello at the Massachusetts...
Top Prompting Strategies Unveiled by Anthropic Experts
Prompt engineering is the bridge between human intention and AI output, and its impact on industries from healthcare to research is profound. As AI systems become more powerful, the ability to craft precise, effective prompts has emerged as a key skill in making these systems work for us. Anthropic’s prompt engineering experts have spent years...
AI was born at a US summer camp 68 years ago. Here’s why that event still matters today.
Imagine a group of young men gathered at a picturesque college campus in New England, in the United States, during the northern summer of 1956. It’s a small casual gathering. But the men are not here for campfires and nature hikes in the surrounding mountains and woods. Instead, these pioneers are about to embark on...
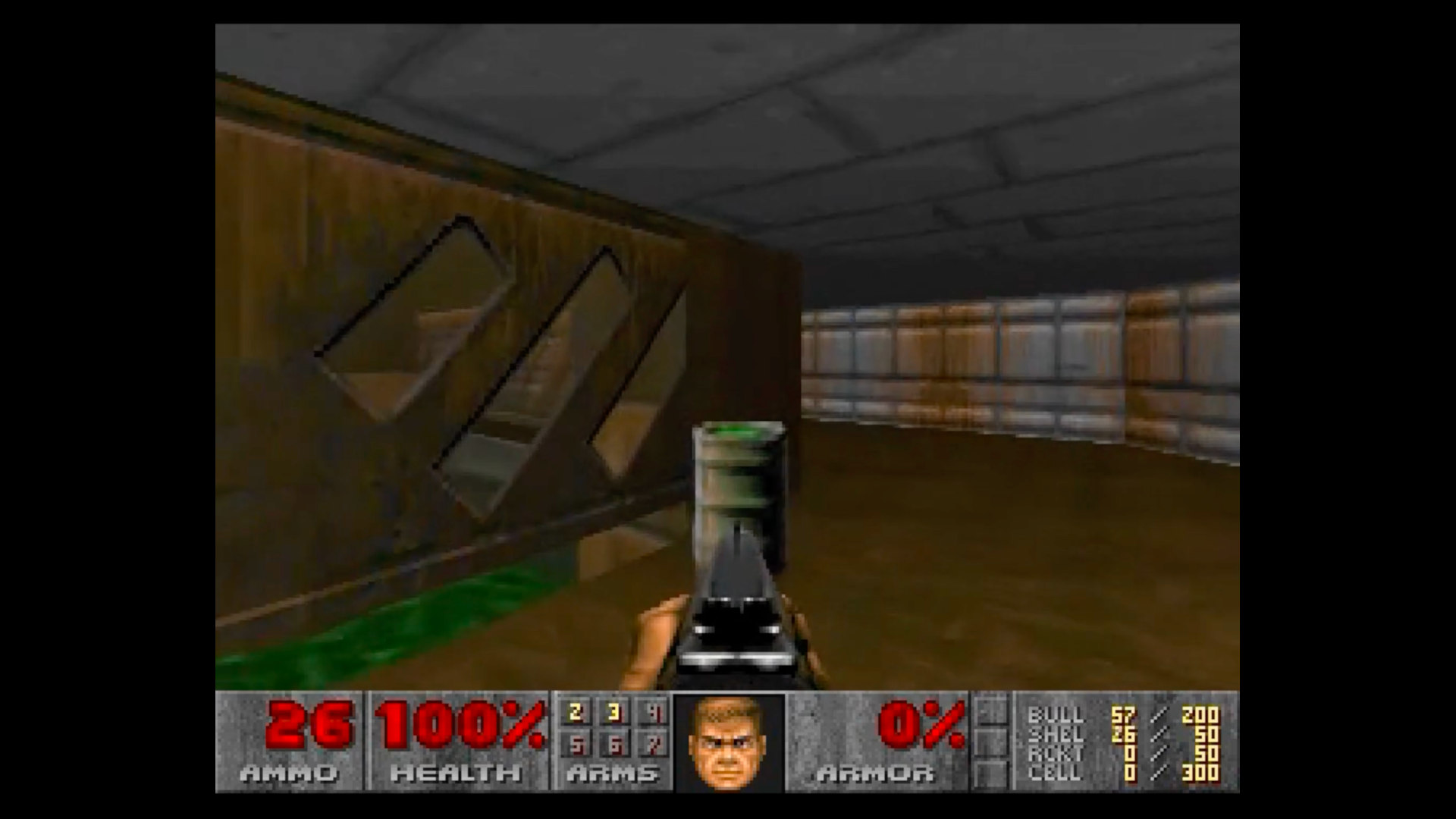
AI Simulates Classic DOOM
Imagine a world where you could play DOOM—yes, the iconic 1993 first-person shooter—powered not by a traditional game engine but by a neural network. Thanks to a groundbreaking new AI system called GameNGen, developed by researchers at Google Research, Google DeepMind, and Tel Aviv University, this is no longer a futuristic dream but a reality....
What is In-Context Learning of LLMs?
In-context learning (ICL) refers to a remarkable capability of large language models (LLMs) that allows these models to perform new tasks without any additional parameter fine-tuning. This learning approach leverages the pre-existing knowledge embedded within the model, which is activated through the use of task-specific prompts consisting of input-output pairs. Unlike traditional supervised learning that...
Do Emergent Abilities in AI Models Boil Down to In-Context Learning?
Emergent abilities in large language models (LLMs) represent a fascinating area of artificial intelligence, where models display unexpected and novel behaviors as they increase in size and complexity. These abilities, such as performing arithmetic or understanding complex instructions, often emerge without explicit programming or training for specific tasks, sparking significant interest and debate in the...
Women are less interested in AI than men, but using it would help them advance at work
Women use generative artificial intelligence tools less than men do. The World Economic Forum recently published an article on the subject. It reported that 59 per cent of male workers aged between 18 and 65 use generative artificial intelligence at least once a week, compared with 51 per cent of women. Among young people aged...
AIs encode language like brains do − opening a window on human conversations
Language enables people to transmit thoughts to each other because each person’s brain responds similarly to the meaning of words. In our newly published research, my colleagues and I developed a framework to model the brain activity of speakers as they engaged in face-to-face conversations. We recorded the electrical activity of two people’s brains as...